Understanding the vulnerability
The best presentation of the vulnerability can be read on the owasp website.
Technical representation
Server-side request forgery is the process of using the vulnerable server (often web-app) as a trusted intermediate to reach internal resources unavailable otherwise.
To do so, the attacker must make a crafted request to the web-app containing a payload aimed at the internal resources. Upon examining sane request made through the website, you might encounter these by stumbling on a parameter that make calls to API or internal servers.
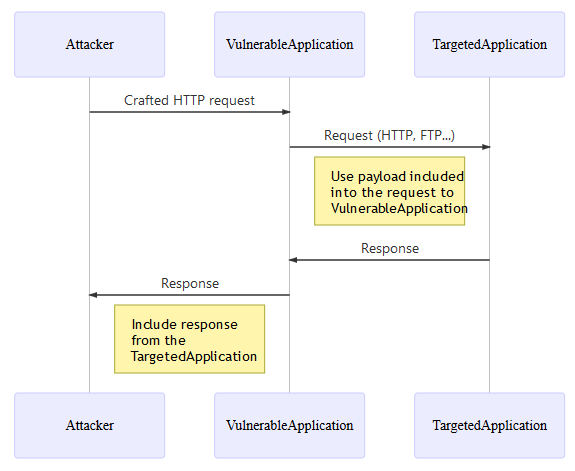
ELI5
An attacker wants to obtain resources (information ; control) locked in an area he cannot access. However, he can ask questions with Alex, an intermediate.
Alex :
- Has access to the restricted area.
- Must answer the questions.
- Can already know the answer, or check in the area if it’s not private.
- Should answer “I’m not allowed to answer” to any question involving protected resources in the area.
The vulnerability arises if Alex is tricked and answer any question related to the area’s sensitive zone.
If the Attacker successfully tricks Alex, the most probable consequences could be the following :
- revealing sensitive information related to the area (information stealing)
- indicating an access entrance to the area
- trick Alex into doing something or making someone do something inside the area (remote control)
Remediation
- White listing can be a solution if the range of retrievable fields is well defined.
- Server-side sanitizing and input verification is mandatory.
- Minimizing attack vectors by avoiding exposing parameters / queries to users.
- Firewall rules from the Server to other systems in the network.
Practicing
Every web-security labs can be found here.The write-ups are mapped on the Portswigger MOC SSRF section.
RootMe has currently 2 SSRF challenges :