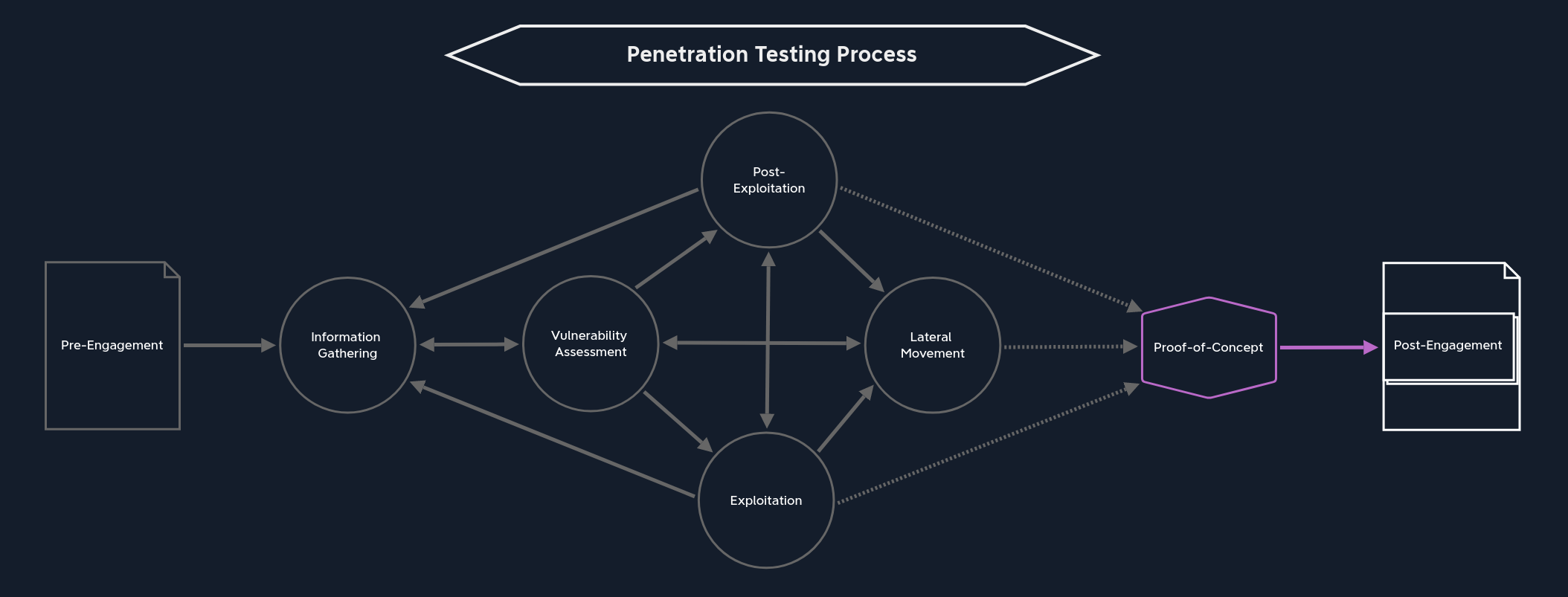
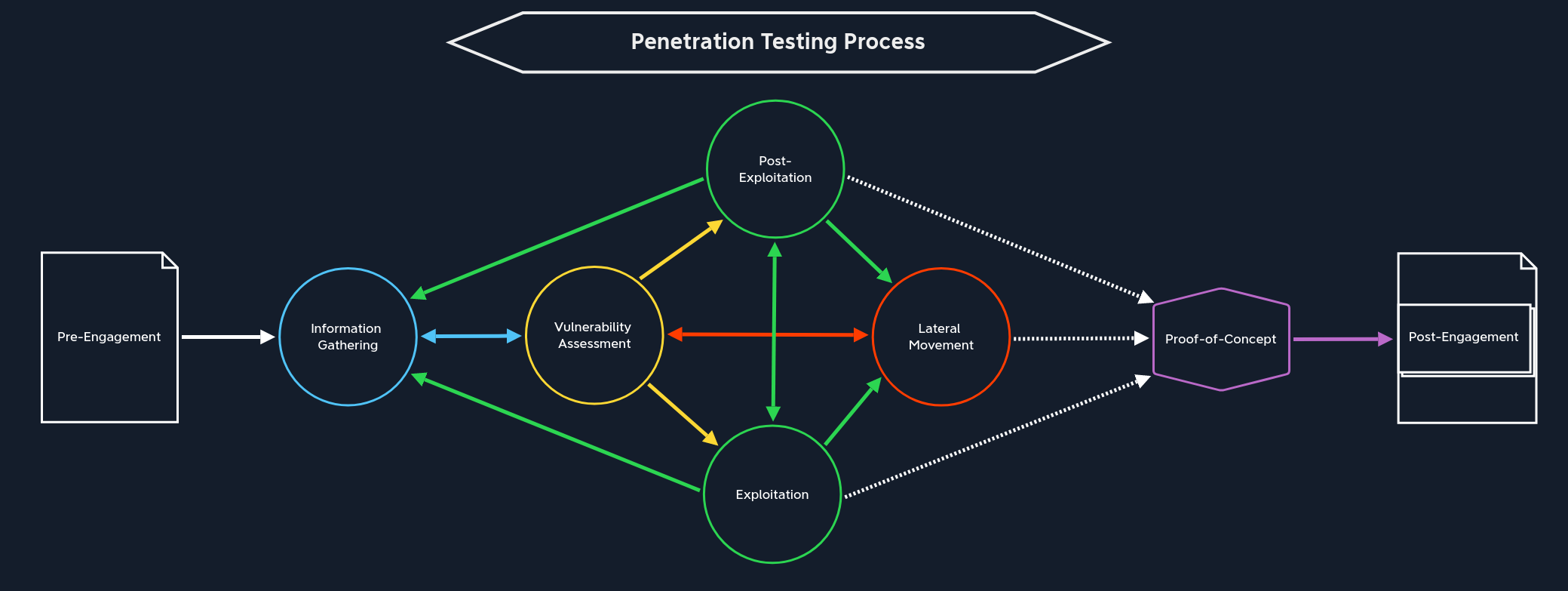
Penetration Testing Phases - Assessment Specific Stages
Pre-Engagement
Skipping as it differs slightly from each mission/company.
Information Gathering
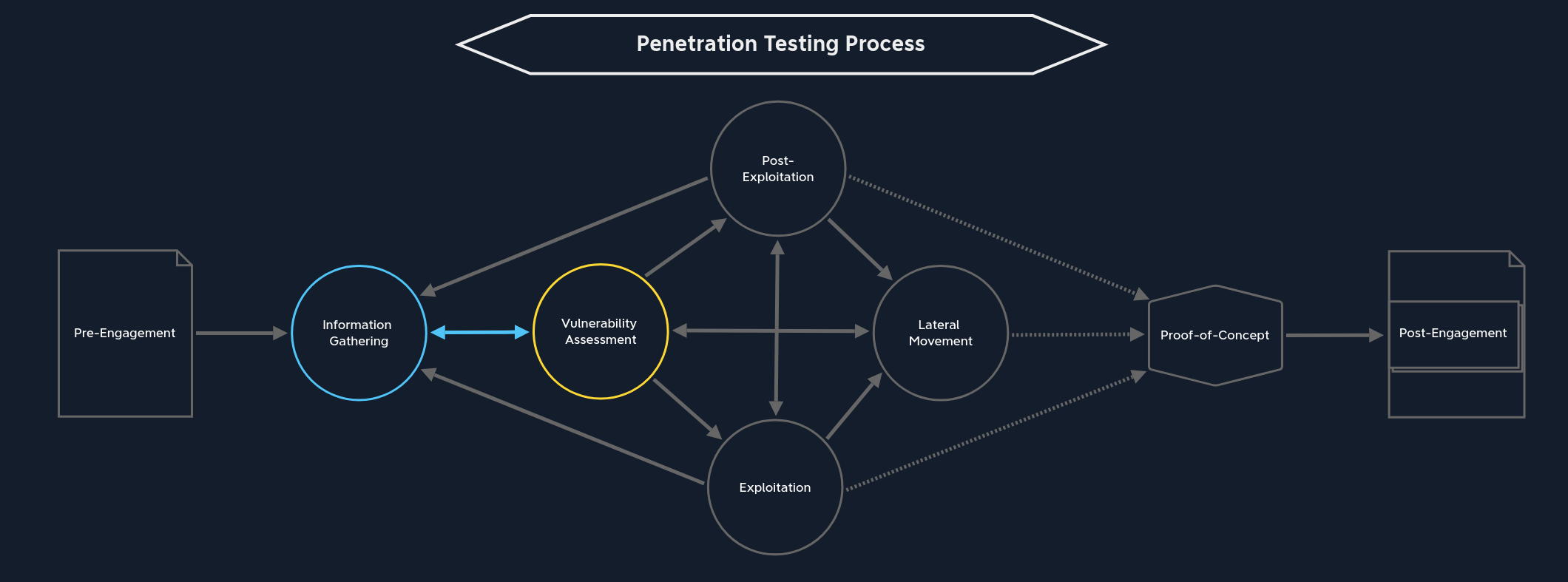
Most topics talked about here will be mentioned again in later modules, so dedicated notes will be made rather than filling directly this note. Since this module is also very verbose, I choose not to follow the usuals sub-paragraphs structure and be more concise.
Open-Source Intelligence
OSINT quick wins
Github
Github repository
Password, SSH Keys, API Keys, exposed code.
Same thing on stackoverflow
Linkedin Profiles
Company members skills are often related to their work mission. Same goes for users, pro mailing etc…
Job Posts
Company posting job with skills and requirements give great insight about the technology they’re using.
Dorks
google dorks are useful to filter out research.
source
Infrastructure Enumeration
Use DNS enumeration to look for Nameservers, Mail Servers, Web Servers, cloud VM …
Service Enumeration
Using Nmap to enumerate services on target. Always think about the context for any service in use/exposed :
- What service ?
- Version
- Usage
- Exposed information
Common services to enumerate
You could already grab sensitive information
Finding old OS and services versions can already give info on potential unpatched vulnerabilities.
Web Enumeration
This is not included in the module listing, but it needs a dedicated note and should be mentioned in an introductory content.
Host Enumeration
Now that the infrastructure has been mapped, you should look for hosts with these questions in mind :
- What OS ?
- Which services ?
- Version
Pillaging
You should retrieve everything possible after Post-Exploitation phase. This includes names, network information, data…
A good pillaging is key
This must be done toroughly since it can be the key difference between a one machine compromission and pivoting with lateral movement. This will very likely be critical for the CPTS exam.
Vulnerability Assessment
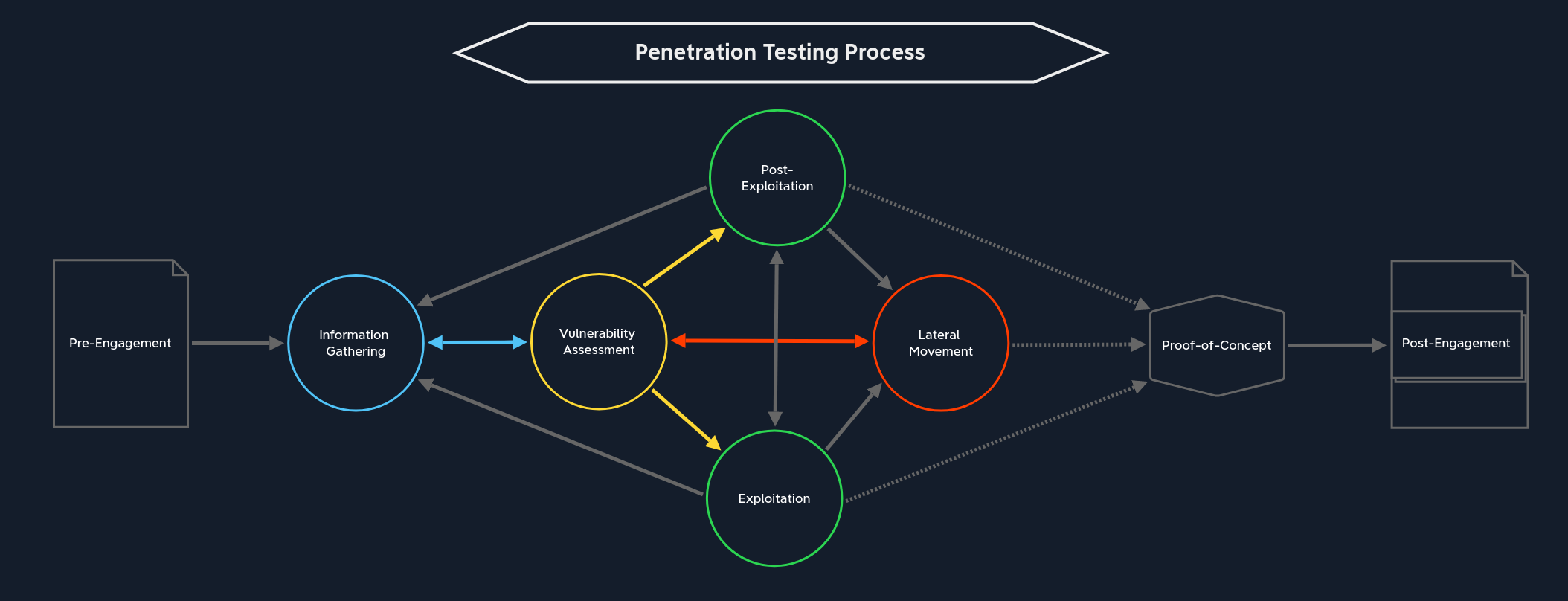
Vulnerability Research
Passive & Active Enumeration can identify vulnerable versions of OS / services vulnerable to Common Vulnerability Exploits. Look for them after identifying a version :
Misconfiguration
Check for known misconfiguration on found target. Trying to exploit these misconfiguration in Exploitation phase. This requires more research on the Internet than CVE.
Add Findings on KB
Create a note for said service and explain the found misconfiguration while dissociating any context from the target when it’s tied to customers.
Exploitation
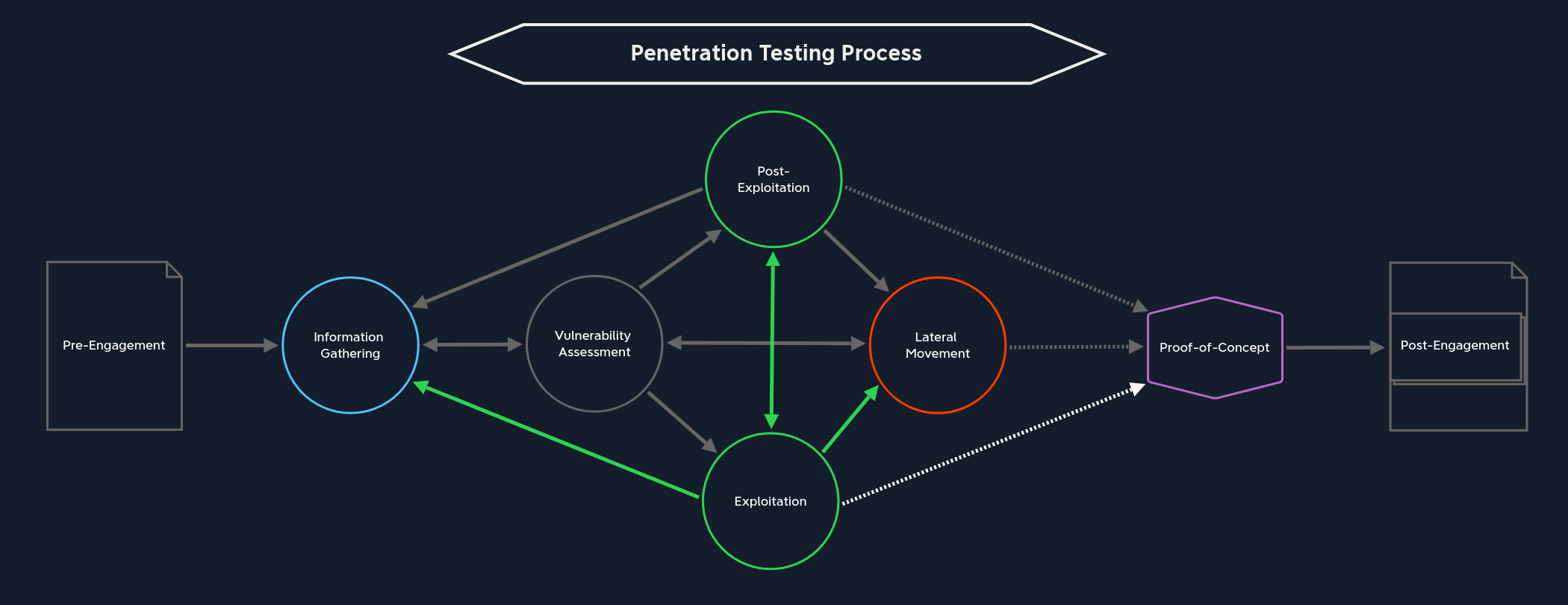
Identify probability of success
- How documented and easy to exploit is the found vulnerability ?
- Does existing exploit exist or do you need to recreate one yourself ?
- Does the vulnerability requires specific conditions
Does the exploit impact the target
- EternalBlue can crash the machine system
- LFI won’t do anything harmful…
Home Lab to replicate environment
See Replicating challenge with home lab
Post-Exploitation
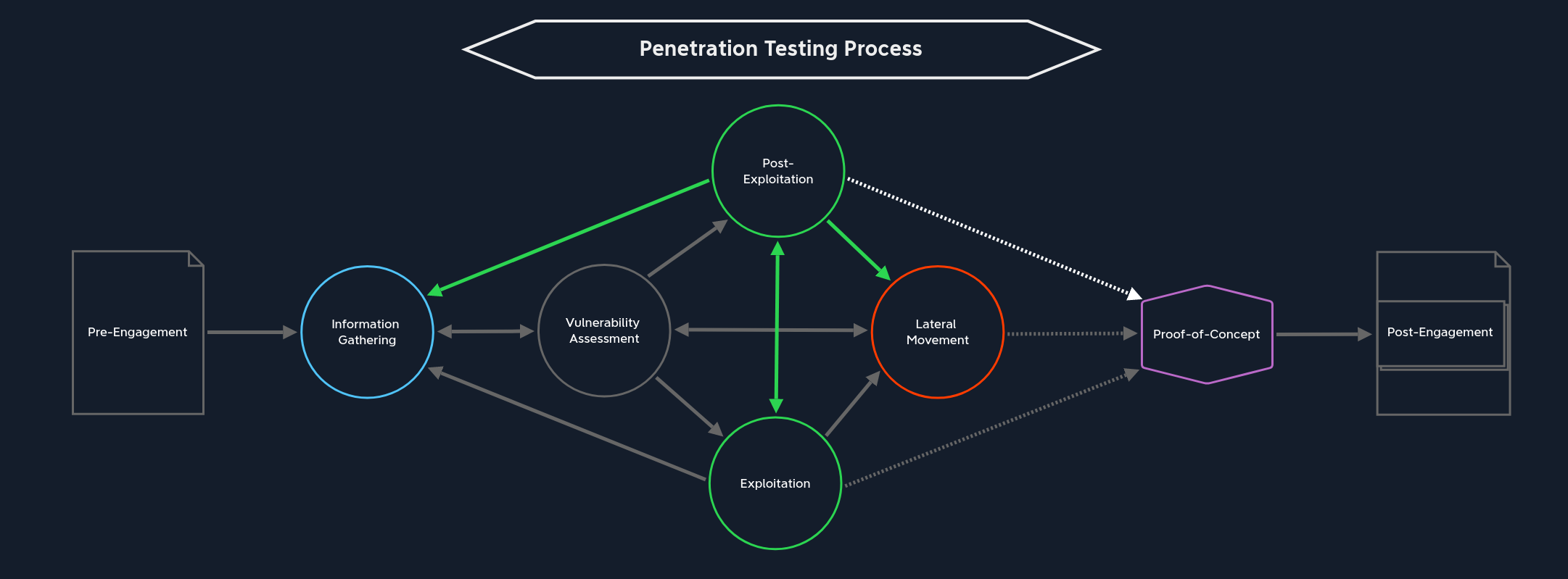 Get back to Information Gathering once we have a foothold in a machine and Pillaging.
Get back to Information Gathering once we have a foothold in a machine and Pillaging.
Avoid flagged payloads and commands. Any monitoring on the target will be trigger upon using whoami net user mimikatz and every basic scripts.
Feedback for the client
It can often help our clients if we run commands or tools that their defenses stop or detect. It shows them that their defenses are working on some attacks. Keep in mind that we are emulating an attacker, so it’s not always entirely bad for some of the attacks to get noticed. Though when performing evasive testing, our goal should be to go mostly undetected so we can identify any “blind spots” our clients have in their network environments. Source : HTB
Persistence
Adding an SSH Key, Setting up Bind Shell or Reverse shell. This will be discussed in more details later.
Privilege Escalation
Increase your privilege as much as possible. Depends on the OS, available resources etc… Dedicated notes will be filled up with respective linux privilege escalation cheatsheet and windows privilege escalation cheatsheet.
Lateral-Movement
Try to get a hold of other machines in the network. This topic will be further investigated in the Pivoting, Tunneling, and Port Forwarding module.
If you succeed at compromising other machines, repeat #Information Gathering, Vulnerability Assessment, Exploitation and Post-Exploitation.
Penetration Testing Phases -Project Closeout
Proof-Of-Concept
 Gather Screenshots of finding, categorize found vulnerabilities.
Gather Screenshots of finding, categorize found vulnerabilities.
Distinguish Vulnerability and Proof
The proof must highlights the underlying vulnerability. Client must understand the root cause of your actions.
Post-Engagement
Cleanup
Keep track of each account you’ve created during the tests, payload you’ve uploaded etc… Everything must be kept in mind for deletion and communicated to the client if you cannot do it yourself.
Documentation and reporting
Report your findings, screenshot everything you get (filter out what ends up in the report at the end). Notes must be succinct but structured enough to allow someone else to write the final report. The structure of the reporting and end result
